All images and animations © 1991-2024 Warren Schirtzinger
It’s Value Creation Aligned with Human Behavior
The most exciting and successful companies deliver the right value, to the right people at the right time. They understand how we define value and what makes us eager to adopt something new.
And the best part is they don’t force us to change the way we live our life. They change their product offering to match our current habits and preferences.
These companies don’t invent a product and then try to sell it. They don’t create a new technology just because it’s cool. And they don’t just give us a trendy new method.
The most exciting companies create and deliver value that sells itself.
It’s a Systematic Approach
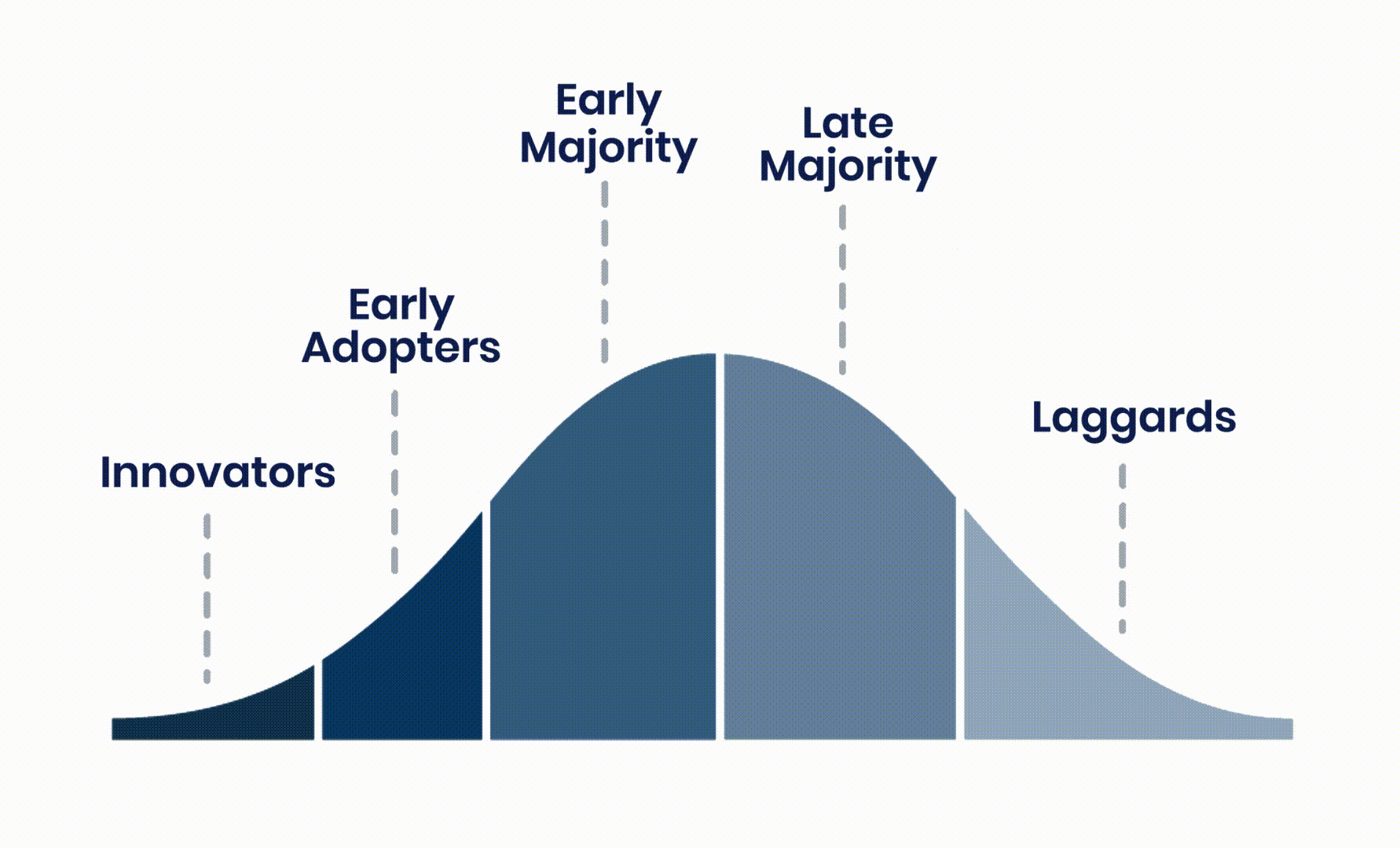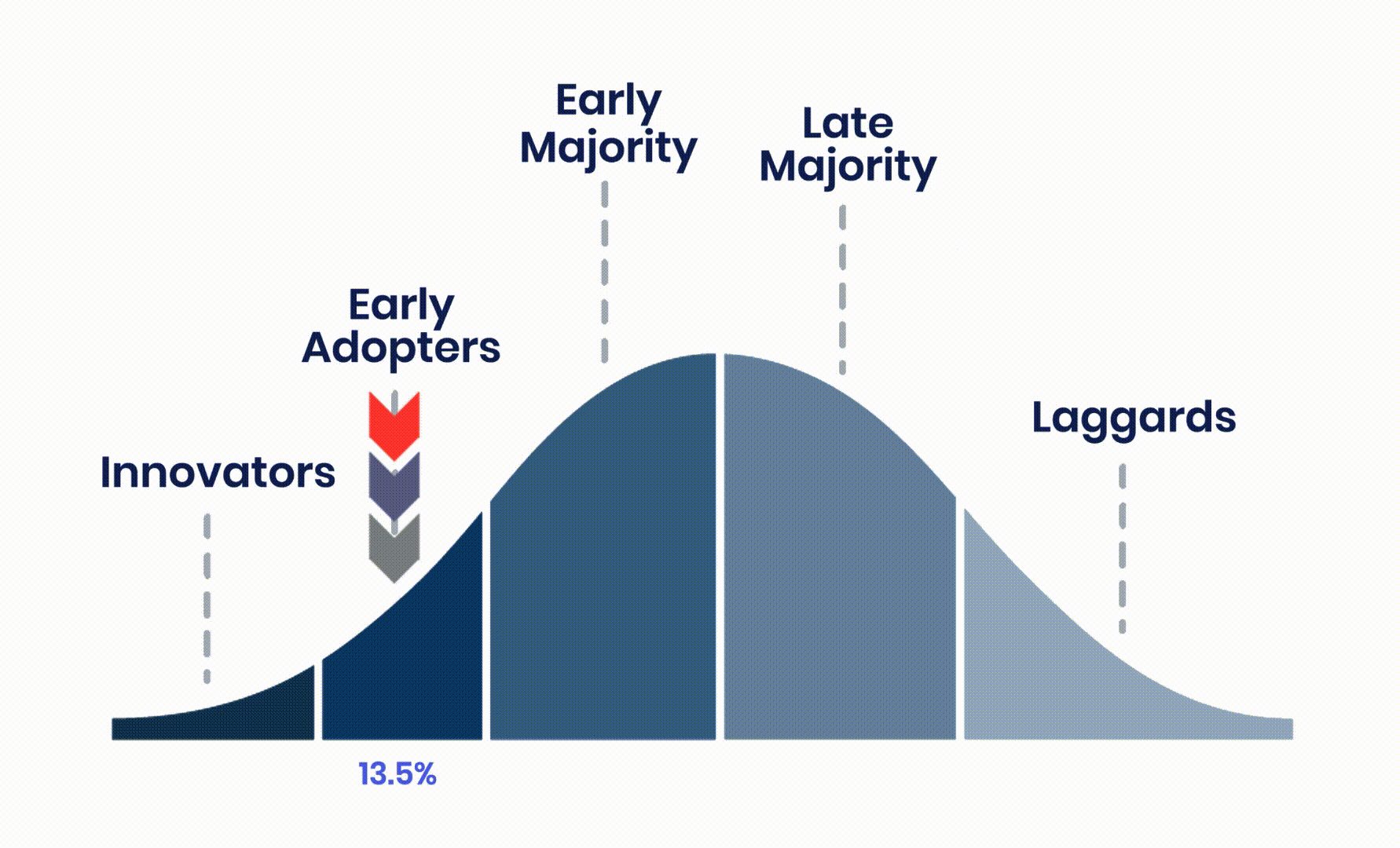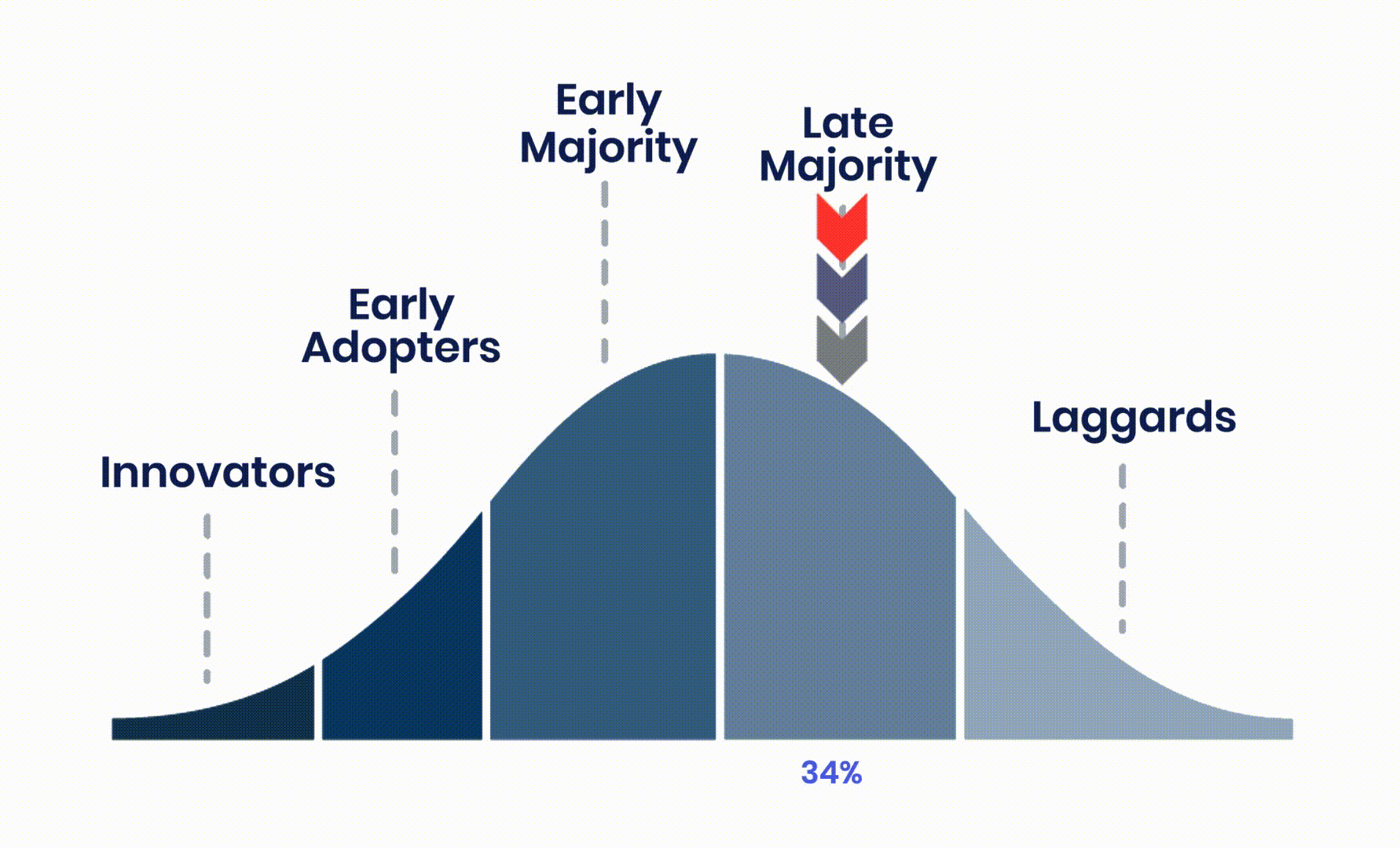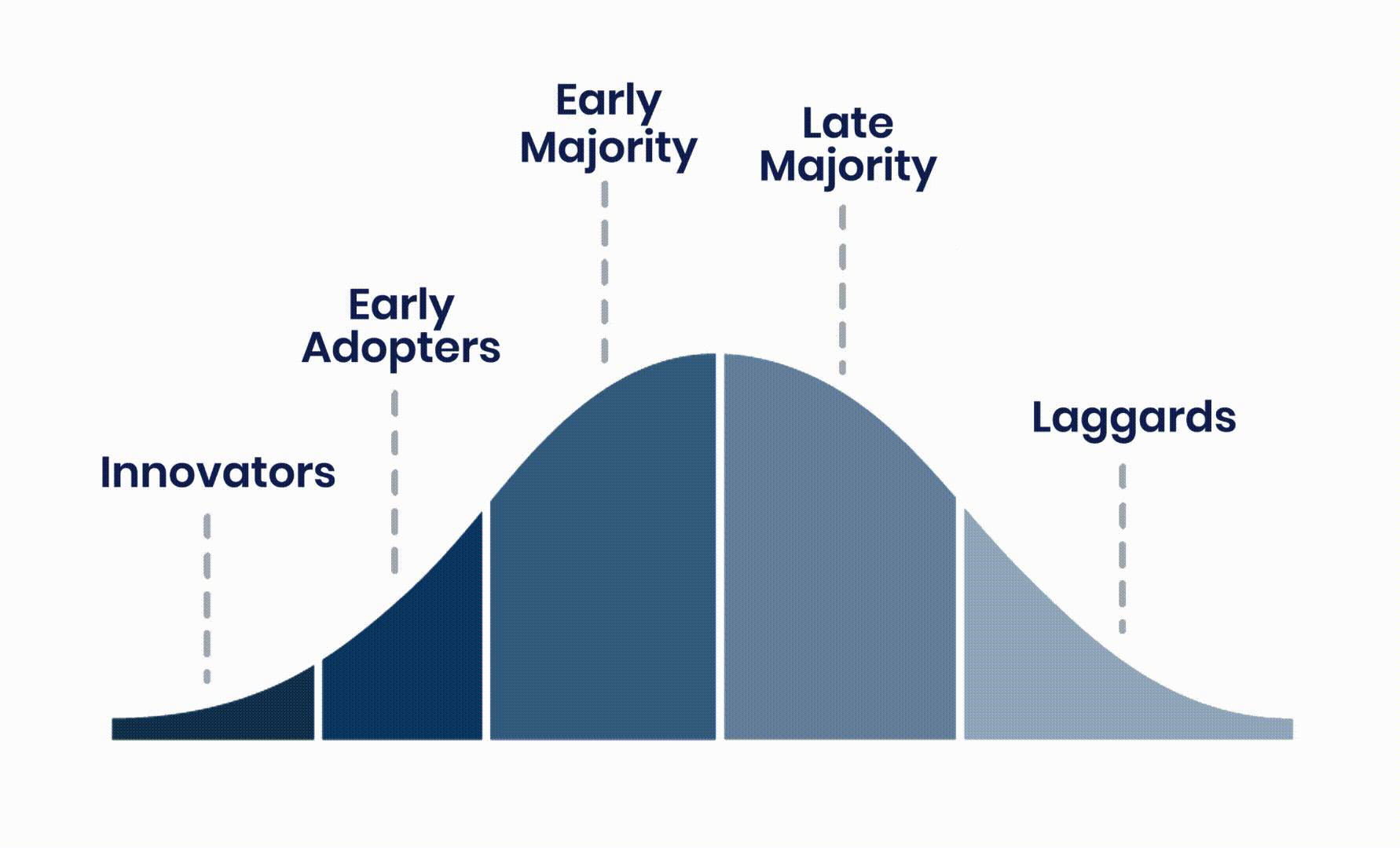
Value Alignment is a process of identifying and describing value before attempting to create it. The journey starts with understanding the people you are trying to serve. These people are a proxy for the level of market maturity and the amount of risk customers are willing to accept. Systematically lowering the perception of risk is what increases value and accelerates adoption.


Legendary Changemakers
Many of the greatest creators and providers of value naturally understand the way humans see and avoid risk. They intuitively know that significant change represents a potential loss of money, time and reputation. Plus, concerns about failure, criticism, and overall happiness keep many people from embracing innovation. Psychological safety plays a critical role in the process of creating, delivering and communicating value.
The Pillars of Value Alignment
Inspired by the work of business strategist Michael Porter, the Value Alignment process consists of the identification of attractive market segments, the delivery of value to the target audience, and effective communication of value using credible methods of proof and social connections that are based on trust .


Backed by Human Psychology
Successful companies create human-centered products that integrate technology with intangible attributes based on social-psychology, community, standards and cooperation. And this means making compatibility, usability, observability, affordability and reliability more important than the core technology itself.
The Building Blocks of
Value Alignment
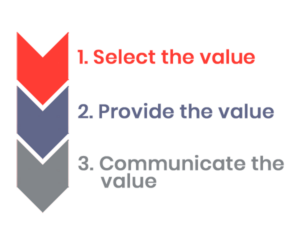
The primary objective of your organization must be to offer a product or service in such a way that it generates value for the customer. And the job of all stakeholders in your company is to create, deliver and communicate value as defined in the following three steps:
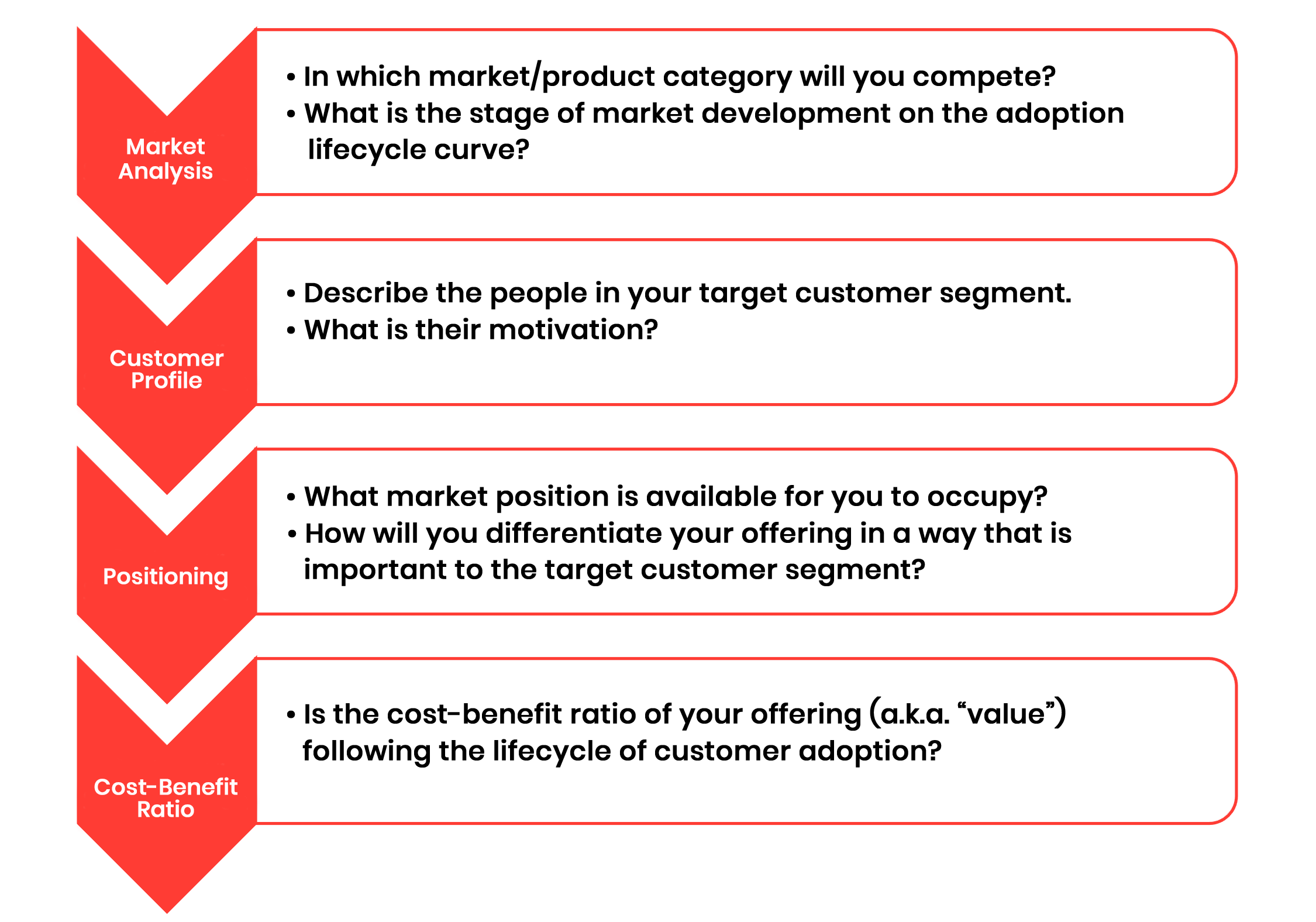
1. Select the Value
Can you identify, based on the lifecycle of adoption, which market segments are most attractive, and which are not? And can you deliver the value required at a compelling cost, while securing a unique competitive position?
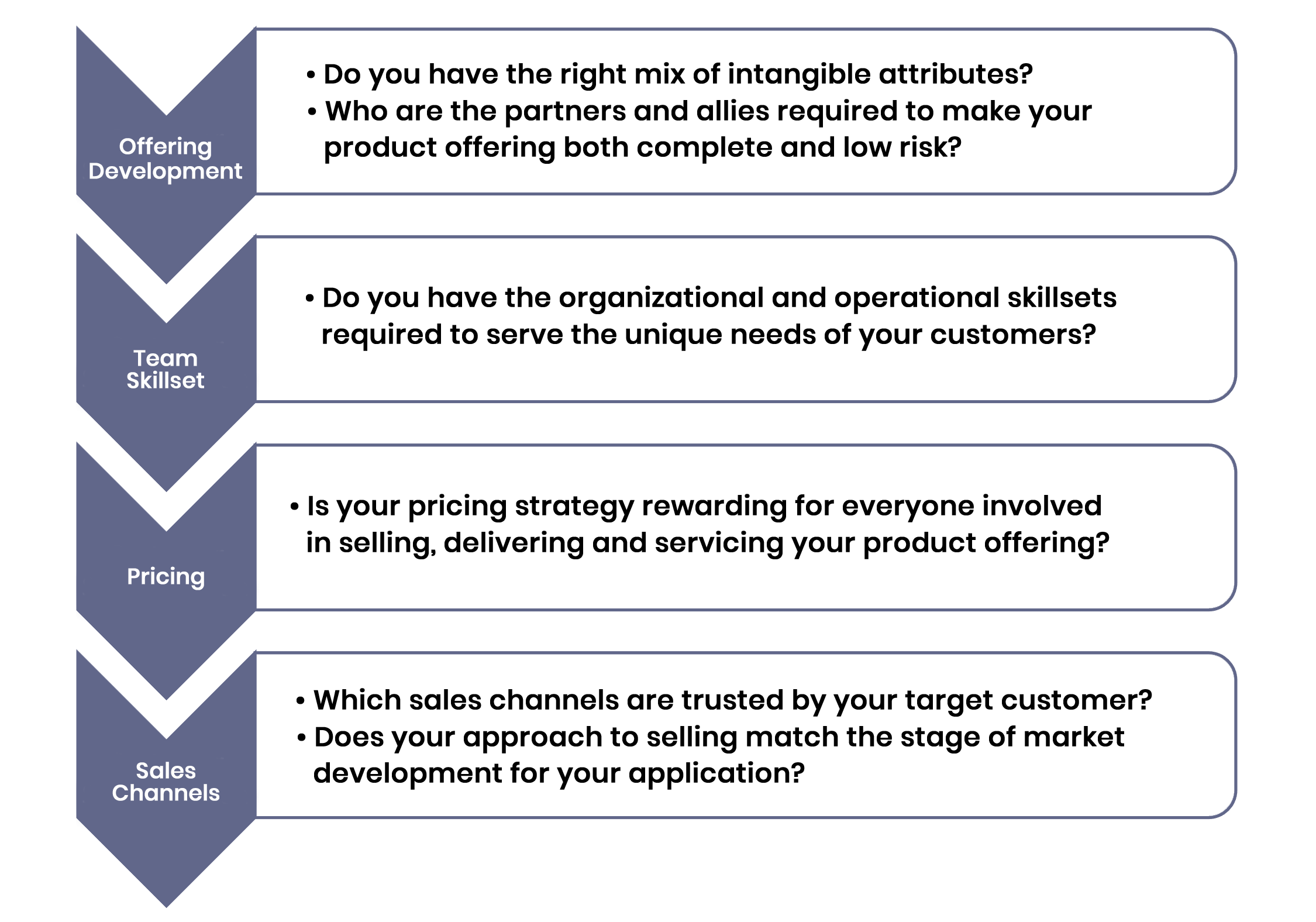
2. Provide the Value
A business is a value delivery system. And your business systems must “echo” the specific value you have selected, to ensure that each activity of the company delivers the right thing at the right time.
3. Communicate the Value
An innovation or a new technology isn’t enough. You need to be able to communicate its value to customers. Communicating value means walking your audience from exposure, to awareness and attention, to understanding, to evaluation and finally to action.

When a company analyzes the market, selects the best opportunities, and positions themselves correctly in the minds of their target segments, they will be able to deliver and communicate value in a differentiated manner that is sustainable.
Approximately half of all new products fail because they force the customer to assemble incompatible and incomplete solutions on their own. Brainstorming, failing fast, and pivoting are attempts to guess what a complete, compelling and low-risk solution might be. But products based on guessing almost never work and are not dependable methods for predictable new product success.
Why risk failure when you don’t have to? It is time to look past the trendy, ineffective shortcuts that have persisted over the years and adopt a proven approach to value creation and delivery.